discussing the policy implications of the findings presented in the UNEP Foresight Brief. Focus on the need for integrated approaches to land management that prioritize vegetation cover, soil health, and water retention. near Colorado – About 15.9 inches (404 mm) per year.
Where to find discussing the policy implications of the findings presented in the UNEP Foresight Brief. Focus on the need for integrated approaches to land management that prioritize vegetation cover, soil health, and water retention. near Colorado – About 15.9 inches (404 mm) per year?
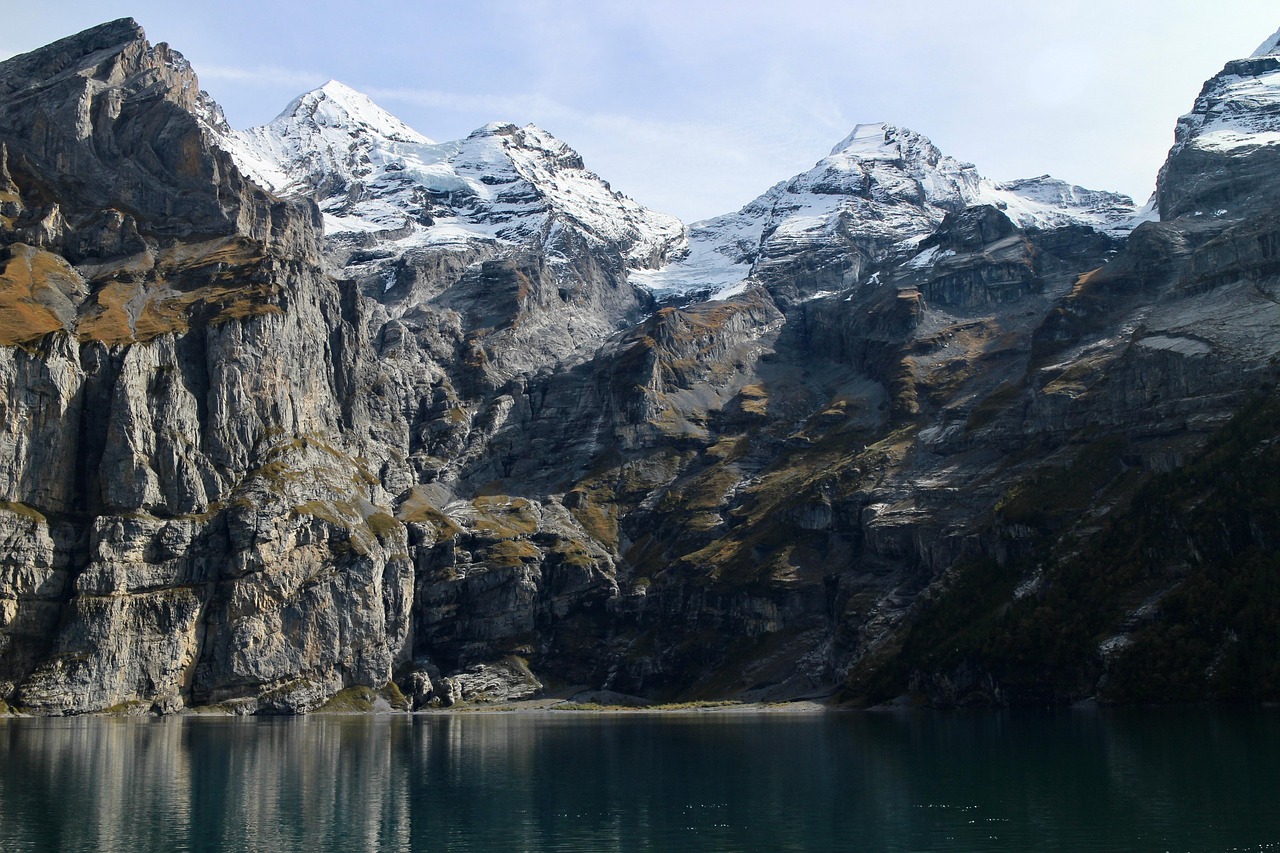
Saving Lake Mead: A Drop in the Bucket Starts with Healthy Land
The Shrinking Lake
Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States, is facing a crisis. This giant lake, behind the iconic Hoover Dam, provides water to millions in the western US, but it’s shrinking at an alarming rate.
How We Can Help:
Slow Down the Flow:
- Building Small Dams & Ponds: Like tiny sponges, these structures can capture rainwater and allow it to soak into the ground instead of rushing off.
Healthy Soil, Healthy Water:
- Boost Soil Health: Healthy soil acts like a giant sponge, holding onto water and preventing it from flowing away.
- Caring for the Land: By taking care of our land, we can keep the water cycle healthy and help fill Lake Mead.
Every Little Bit Counts
Together, we can make a difference. By implementing these simple solutions, we can help keep Lake Mead full and secure water for the future.
Saving Our Water: How Better Land Management Can Help Lake Mead
TL;DR: Lake Mead, the largest reservoir in the United States, is shrinking. But we can help! By taking care of the land, we can save water and keep Lake Mead full. This means planting more trees, keeping soil healthy, and making sure water stays in the ground instead of running away.
The Shrinking Lake
Lake Mead is a giant lake behind Hoover Dam, providing water to millions of people in the western United States. But lately, the lake has been shrinking. Why? Less rain and hotter weather are making the water evaporate faster. The Colorado River, which feeds Lake Mead, is also getting less water due to climate change.
What Can We Do?
The UNEP Foresight Brief, a report by the United Nations Environment Programme, says we need to take better care of the land. Here’s how:
H2: Prioritizing Vegetation Cover:
- More Trees, More Water: Trees act like giant sponges, soaking up rainwater and releasing it slowly. This keeps water in the soil, where it can be used by plants and trees. Planting more trees, especially in areas that have been cleared, can help us save water.
H2: Soil Health:
- Healthy Soil, Healthy Water: Healthy soil can hold more water and prevent it from running off into rivers and streams. When soil is healthy, plants can grow better, which helps to keep the water cycle going. Farmers can use techniques like no-till farming and crop rotation to keep soil healthy.
H2: Water Retention:
- Slowing Down Water: Water retention techniques, like building small dams and ponds, can help slow down water flow and allow it to soak into the ground. This helps keep more water available for plants and keeps the water cycle healthy.
The Active Climate Rescue Initiative
The Active Climate Rescue Initiative (ACRI) is an organization that helps people understand and use climate solutions. They focus on technologies and methods that help us manage land better, like:
- Regenerative Agriculture: Farming that works with nature to improve soil health and increase water retention.
- Watershed Restoration: Projects that bring back healthy ecosystems in areas where water is important, like rivers and wetlands.
- Climate-Smart Forestry: Planting trees in a way that benefits both the environment and people.
Summary
Lake Mead is an important source of water, but it’s facing challenges from climate change. By taking care of the land, we can help keep the water cycle healthy and keep Lake Mead full. This means prioritizing vegetation cover, keeping soil healthy, and using water retention techniques. Organizations like the Active Climate Rescue Initiative can help us learn more about these solutions and put them into action. By working together, we can protect our water resources and create a healthier future.
More on discussing the policy implications of the findings presented in the UNEP Foresight Brief. Focus on the need for integrated approaches to land management that prioritize vegetation cover, soil health, and water retention.…
- ## Important: UNEP Foresight Brief, Integrated Land Management, Lake Mead
- UNEP Foresight Brief:
- UNEP Foresight Brief Policy Implications
- UNEP Foresight Brief Land Management
- UNEP Foresight Brief Vegetation Cover
- UNEP Foresight Brief Soil Health
- UNEP Foresight Brief Water Retention
- UNEP Foresight Brief Sustainability
- UNEP Foresight Brief Environmental Policy
- UNEP Foresight Brief Climate Change
- UNEP Foresight Brief Biodiversity
- Integrated Land Management:
- Integrated Land Management Policy
- Integrated Land Management Approaches
- Integrated Land Management Strategies
- Integrated Land Management Practices
- Sustainable Land Management
- Ecosystem Services
- Land Use Planning
- Land Degradation
- Soil Erosion
- Water Scarcity
- Vegetation Cover:
- Vegetation Cover Restoration
- Vegetation Cover Management
- Vegetation Cover Benefits
- Vegetation Cover and Soil Health
- Vegetation Cover and Water Retention
- Reforestation
- Afforestation
- Agroforestry
- Soil Health:
- Soil Health Management
- Soil Health Indicators
- Soil Carbon Sequestration
- Soil Fertility
- Sustainable Agriculture
- Conservation Agriculture
- No-till Farming
- Soil Erosion Control
- Water Retention:
- Water Retention Strategies
- Water Retention Techniques
- Water Retention in Arid Regions
- Water Harvesting
- Water Conservation
- Drought Mitigation
- Water Management
- Lake Mead:
- Lake Mead Water Levels
- Lake Mead Drought
- Lake Mead Reservoir
- Lake Mead Water Crisis
- Colorado River Basin
- Water Shortages
- Water Allocation
- Water Conservation Efforts
- Lake Mead Recreation
- Lake Mead History
- Combined:
- UNEP Foresight Brief Lake Mead
- Integrated Land Management Lake Mead
- Vegetation Cover Lake Mead
- Soil Health Lake Mead
- Water Retention Lake Mead
- Lake Mead Policy Implications
- Lake Mead Sustainability
- Lake Mead Conservation
- Lake Mead Water Management
- Long-Tail Keywords:
- The policy implications of the UNEP Foresight Brief on land management for Lake Mead
- How integrated land management approaches can improve water retention in Lake Mead
- The importance of vegetation cover for soil health and water retention in the Lake Mead region
- Sustainable land management practices for mitigating the effects of drought on Lake Mead
- The role of UNEP Foresight Brief in shaping land management policies for Lake Mead
- The impact of climate change on Lake Mead water levels and the need for integrated land management
- The economic and social implications of the Lake Mead water crisis and the role of sustainable land management
- Case studies of successful integrated land management practices in the Lake Mead region
- The future of Lake Mead: challenges and opportunities for sustainable land management
Contents
- 1 Where to find discussing the policy implications of the findings presented in the UNEP Foresight Brief. Focus on the need for integrated approaches to land management that prioritize vegetation cover, soil health, and water retention. near Colorado – About 15.9 inches (404 mm) per year?
- 2 Saving Lake Mead: A Drop in the Bucket Starts with Healthy Land
- 3 Saving Our Water: How Better Land Management Can Help Lake Mead
- 4 More on discussing the policy implications of the findings presented in the UNEP Foresight Brief. Focus on the need for integrated approaches to land management that prioritize vegetation cover, soil health, and water retention.…